

The biosynthesis step in which the cyclic peptide backbone is formed involves an asparaginyl endopeptidase, of which in C.
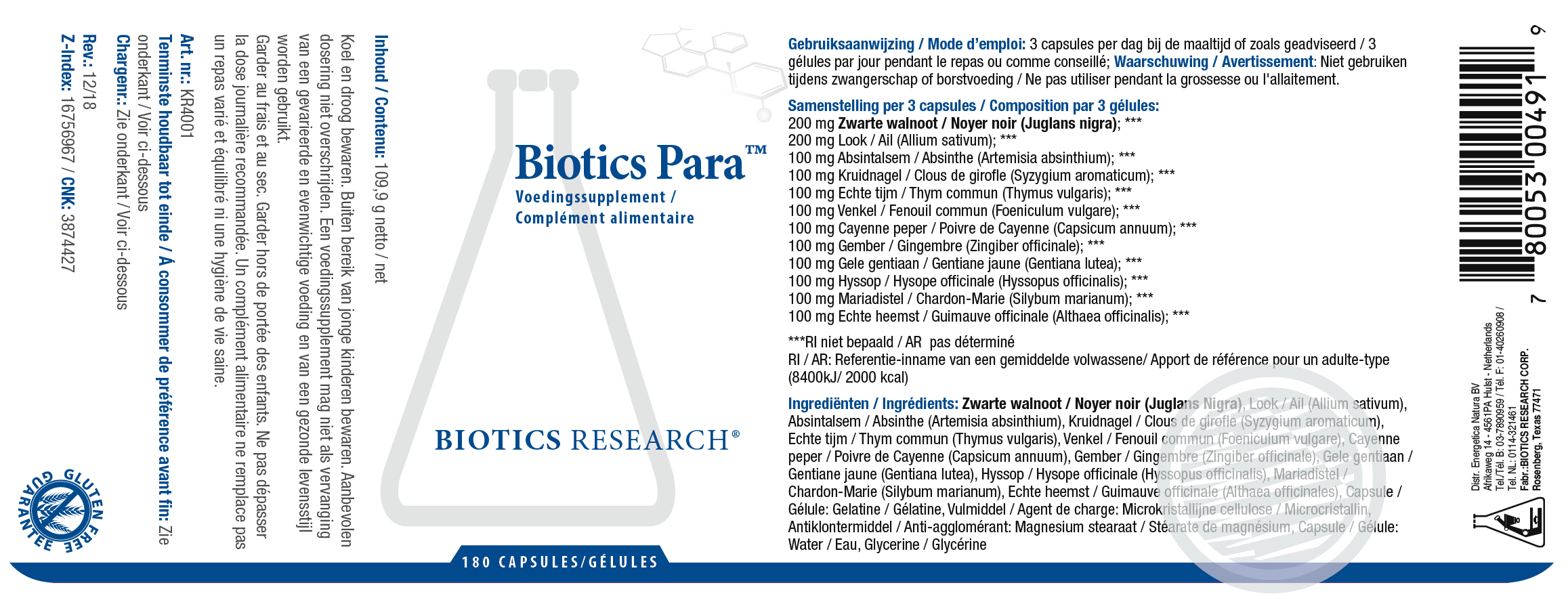
We include a description of the genetic origin of these peptides, which interestingly involve the co-option of an ancestral albumin gene to produce the cyclotide precursor protein. The latter are potent insecticidal molecules and are implicated as the bioactive agents in a plant extract used commercially as an insecticide. ternatea flowers their characteristic blue color, and cyclotides, ultra-stable macrocyclic peptides that are present in all tissues of this plant. Notable amongst its repertoire of chemical components are anthocyanins which give C.
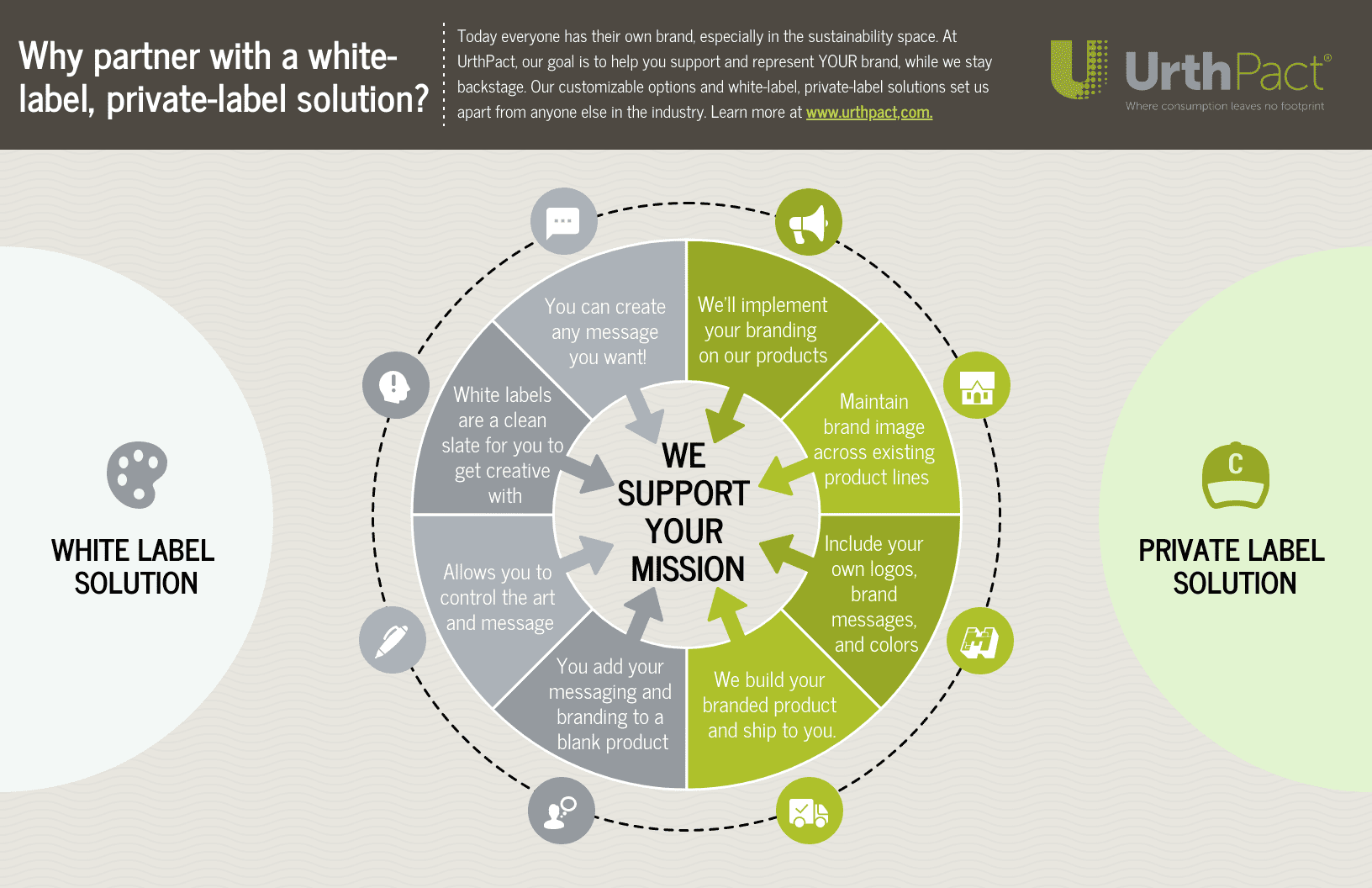
In this article we provide a broad multidisciplinary review that includes descriptions of the physical appearance, distribution, taxonomy, habitat, growth and propagation, phytochemical composition and applications of this plant. The perennial leguminous herb Clitoria ternatea (butterfly pea) has attracted significant interest based on its agricultural and medical applications, which range from use as a fodder and nitrogen fixing crop, to applications in food coloring and cosmetics, traditional medicine and as a source of an eco-friendly insecticide. Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, QLD, Australia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
